A recent report from Humanities Indicators, a project of the American Academy of Arts & Sciences, showed that less than a quarter of Americans aged 18 years or older visited a historical park or monument in 2012—a 13 percentage point drop from 1982. As a student from Brigham Young University (BYU) in Utah, I traveled to Washington, DC, in January to intern with the American Historical Association for the spring semester. Having taken advantage of opportunities to explore the city’s many historic sites and museums, the report made me wonder about the nation’s declining interest in visiting historical sites. This in turn led me to ask the following question: Why should one visit a national historic site, and what can one learn from visiting them?

Standing on Little Round Top, students examined the rocky terrain and the view from the hill in order to better understand battle tactics. Credit: Ryan Baldwin
It was with these questions in mind that I, along with 30 other interns from BYU, traveled to the Gettysburg National Military Park in Pennsylvania to visit the historic site of the Battle of Gettysburg (July 1863). The battle, one of the bloodiest during the American Civil War, is remembered for the Union’s decisive victory over Confederate forces led by General Robert E. Lee. The three-day battle ended with close to 52,000 casualties and inspired President Lincoln’s famous Gettysburg Address four months later.
Managed by the National Park Service, the Gettysburg National Military Park includes a Museum and Visitor Center that allows visitors to watch a film on the Civil War as well as view exhibits and archives related to the battle. While at the museum, we saw the famous Gettysburg Cyclorama—a 42-foot-tall, 377-foot-wide painting that depicts the third and final day of the battle. Our visit also consisted of a guided tour of the historic Gettysburg battlefield. We climbed Little Round Top—a small rocky hill that played a crucial role in the battle—and stood where Union soldiers must have as they watched the Confederate infantry emerge from the trees on the last day of the battle (Pickett’s Charge). We also visited the Gettysburg National Cemetery, which serves as the final resting place for over 3,500 Union soldiers and where President Lincoln delivered the Gettysburg Address.
As we toured the battlefield, I realized that visiting historical sites can not only enrich our understanding of a particular historical event, but it can also allow us to engage with history in a way that provides greater local contextualization and a visceral connection to the people who lived through it. In fact, visiting the military park brought the Battle of Gettysburg alive to me in a way that no textbook had been able to until that point. Seeing the collections and reading archival sources such as journal entries and letters available at the museum allowed me to not only imagine life during the Civil War, but also to reflect on the struggles and experiences of soldiers who fought in the war.
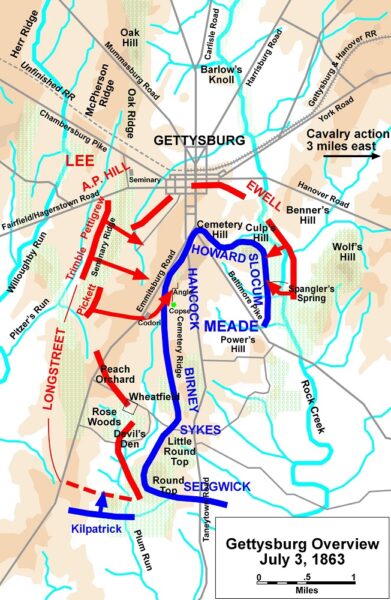
A map of Union and Confederate forces on the day of Pickett’s Charge. Credit: Wikimedia Commons
Similarly, visiting the actual location helped me better understand the logic and tactics deployed by both sides during the battle, and to come to terms with the immense loss of life that had occurred there. It is hard to visit a site as historic and significant as Gettysburg and not feel a connection to the men and women of the past, as well as to develop a deeper appreciation of the significance of the battle and the Civil War to American history and identity.
Visiting the Gettysburg battlefield and seeing the actual geography and landscape of the area, for example, gave me an insight into how historians analyze military tactics. As we stood gazing at Seminary Ridge from the Union center, we could better visualize Pickett’s Charge. Recalling the sources we had read at the museum, my cohort and I discussed the tactics of General Lee’s plan. Students stood on the higher ground and pointed to the open field—a little over three-quarters of a mile long—claiming that the plan was foolish from the start. Others noted how the distance of both Union flanks from their location stretched for a mile in both directions, and commented on the difficulty of moving Union troops and artillery to the center in a short amount of time due to the hills, trees, and other obstacles on either side of their position.
While standing on Little Round Top, students could also see the battlefield for miles, which helped us understand why Union Brigadier General Gouverneur Warren rushed to arrange a defense on the hill during the second day of the battle, an action that heavily contributed to the Union victory. While students often read how Little Round Top was a strategic position due to the high ground, it is difficult to see just how advantageous this spot was without seeing the rocky terrain and the view from the hill firsthand. Seeing and walking the landscape of Gettysburg helped students, including myself, to better understand the battle.
Our final stop for the trip was the National Cemetery where President Lincoln delivered his famous Gettysburg Address. While we stood near the Gettysburg Address Memorial, one of our classmates stood and read the famous speech. At the end of a long day, after having spent so much time reading various sources and seeing the battlefield firsthand, visiting the cemetery allowed for a quiet moment of reflection on the battle, its causes, and its consequences. While I’ve read the Gettysburg Address multiple times throughout my education, this speech never meant more to me than at that moment when I stood at the National Cemetery and pondered at the number of lives lost during the battle.
Regardless of our fields of study or interests, visiting historical sites can lead to a deeper engagement with historical events and give us an opportunity to develop a fuller appreciation for those who lived before us. When taken seriously, these experiences can be invaluable.
This post first appeared on AHA Today.
Ryan Baldwin is a senior studying history with a minor in classics at Brigham Young University. He was the publications intern for the American Historical Association for the spring 2016 semester.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License. Attribution must provide author name, article title, Perspectives on History, date of publication, and a link to this page. This license applies only to the article, not to text or images used here by permission.


