By some metrics, history is trending. Videos shared with the hashtag #HistoryTok have racked up more than six and a half billion views on the social media platform TikTok; in early 2023, a single viral video tagged #HistoryRepeats inspired more than 800,000 users to record their own imagined conversations with distant ancestors. Controversies in the headlines keep sparking vibrant and nuanced public conversation about the historical contexts that shape our contemporary world. And there is much evidence to indicate that students want to know more about the history behind today’s headlines.
Compare this public enthusiasm for history with our discipline’s shifting status in higher education. Since 2016, the AHA has surveyed history departments across the United States to track the total number of undergraduate students enrolling in history courses at their respective institutions. This data indicates an overall decline in history enrollments but leaves many questions unanswered.
The AHA’s 2023 survey of undergraduate history enrollments shows a 2.7 percent decline in the number of enrollments in 2022–23, compared to the previous academic year. The reported decline occurred even as overall undergraduate enrollment at four-year public and private not-for-profit institutions in the United States increased by 0.6 percent in fall 2023 from the year before, according to the National Student Clearinghouse Research Center. This trend is occurring alongside a longer-term decline in undergraduate history degree completions, which the Department of Education reports fell another 6.43 percent in 2022, the most recent year for which data is available.
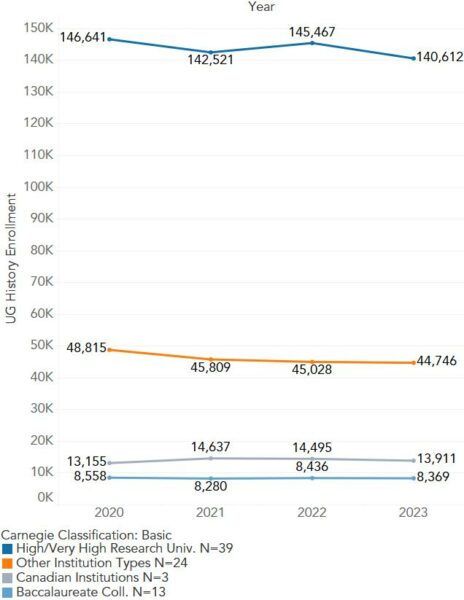
Fig. 1: Undergraduate history enrollment, 2020–23. AHA internal data
This eighth annual survey of history enrollment was conducted online from July through mid-October 2023. The AHA solicited voluntary participation from more than 400 departmental chairs and administrative points of contact. The survey prompted respondents to input the number of undergraduate enrollments in their institution’s history courses for the past four years (2019–20, 2020–21, 2021–22, and 2022–23). This data (Fig. 1) illustrates one symptom of the many pressures undermining the health of history programs at North American universities, but the small number of responses demands cautious interpretation.
The direction in which history enrollments have trended is clear; the causes for this shift and the most effective strategies for improving recruitment and retention are less straightforward. It is vital that all undergraduate students continue to have access to high-quality history education as part of a comprehensive college curriculum.
The downward trend may have paused at some institutions during the pandemic and has now resumed, but less universally.
Out of more than 1,300 institutions in the United States and Canada, 79 colleges and universities contributed numerical data to the AHA’s 2023 enrollment questionnaire. This total includes 75 four-year colleges and universities and one two-year college in the United States, as well as three Canadian universities. Taken together, the responses showed that history course enrollment had declined 2.7 percent in 2020–21, risen 1 percent in 2021–22, and again declined 2.7 percent in 2022–23. Over the entire period, the number of student enrollments reported in 2022–23 was 4.4 percent lower than those for 2019–20. When public and private institutions are disaggregated, we see the only annual percentage growth was among public institutions in the 2020–21 school year, presumably related to unusual student course-taking patterns and the easing of pandemic restrictions on many campuses.
Declines led advances throughout the past four years but with wide variation (Fig. 2). Looking at the change in enrollment from the prior year, in 2020–21, 57 institutions saw falling student numbers and just 22 saw gains, while in 2021–22 enrollment fell at 43 institutions but rose at 36. Last year, 50 programs shrank while 29 grew. This suggests that the downward trend may have paused at some institutions during the pandemic and has now resumed, but less universally. Comparing the first and last years of the covered period, 25 of the responding institutions had higher enrollment in the 2022–23 year than in the 2019–20 year, while 54 served fewer undergraduates last year than they taught three years earlier.
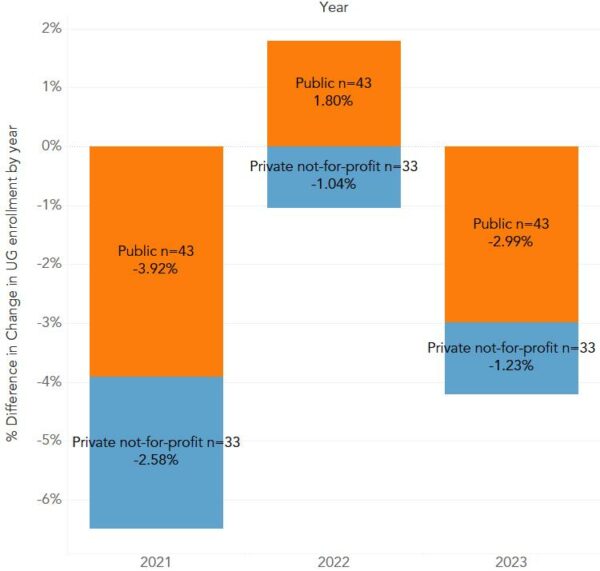
Fig. 2: Change in history enrollment by control and year. AHA internal data
Reports from chairs and other faculty provide insight into how broader national forces have played out in local contexts. The impression among departments where enrollment has declined significantly and consistently is of a landscape where institutional priorities in other fields (preprofessional and/or STEM oriented) have left history departments with shrinking capacity to meet even existing student demand and limited ability to recruit students or market current offerings. One respondent at a midwestern regional public university, where history course enrollment crashed 45 percent over four years, observed that their reduction in enrollment corresponded to a reduction in faculty and thus the inability to offer as many courses. Another regional public institution in the Midwest reported that their total enrollment was down primarily because of lost faculty, but that the number of history majors had rebounded in the past year. One respondent in the Northeast lamented that many faculty expected the already-overworked department chair to address this issue without much buy-in from colleagues. There, enrollment was down more than 13 percent after falling nearly 10 percent the year before.
An individual department’s strategies can still have an effect.
Based on the survey responses, general education reform has continued to erode mandates for history education, but the pace of such reform initiatives might have slowed. And despite a long-term pattern of contraction due to structural shifts in how and why people go to college, an individual department’s strategies can still have an effect. These actions might include things like ensuring that popular classes are offered to students regularly, supporting first-time history students’ learning and progress to degree so that they can return to take another course in the department, and implementing an active recruitment program with marketing on campus and online. Another fruitful avenue for some history departments can be direct communication with academic advisors across campus about the features and benefits of their history offerings for students in other programs and majors.
These local perceptions of what is happening in history departments are vital to identifying important, larger questions that go beyond just numbers. Local awareness combined with broad-based data can help to reveal promising ways to reverse negative trends and suggest the best places to put limited resources to build on program strengths. The AHA will continue its efforts to support history enrollment by advocating publicly for the value of what students learn, communicating data and information about structural changes that impact history departments, and sharing successful models from individual departments.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License. Attribution must provide author name, article title, Perspectives on History, date of publication, and a link to this page. This license applies only to the article, not to text or images used here by permission.

