The AHA’s “Where Historians Work” is an ambitious research project designed to track the career outcomes of everyone who earned a PhD in history from 2004–13 in the United States. Last year, we launched a beta version of “Where Historians Work” showing initial results from 34 PhD programs. Since then, we have gathered information on the remaining 127 PhD programs, locating some 8,000 individuals using publicly available information. We are now in a position to truly understand the national landscape of employment for history PhDs.
Later this spring we’ll publish a series of interactive visualizations that highlight what we have learned about historians and their careers, while allowing users to ask research questions about the data. As we’ve gathered data, we’ve published several blog posts on our findings, focused on describing the incredible range of careers we have discovered in the data. This post focuses on the geography of historians with a PhD, bringing a new and more literal sense of where historians work into the mix.
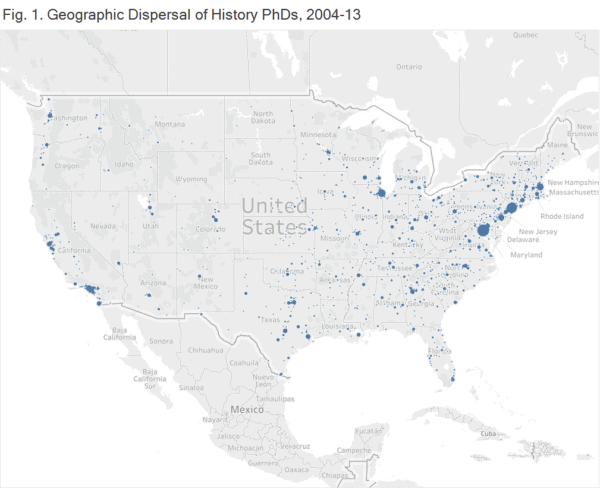
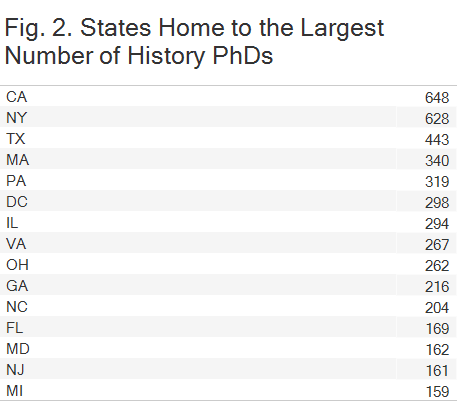
Unsurprisingly, perhaps, the geography of history PhDs closely replicates population patterns in the United States, making “the same places everyone else does” the most straightforward answer to the question of where historians work. History PhDs congregate in high population states: of the 15 most populous states, only Washington and Arizona are not also among the top 15 for employing PhDs from our cohort. (For state population, visit census.gov.)
Another clear pattern is that states that award the largest numbers of history PhDs, many of which have high populations overall, tend to also employ them in the largest numbers. Fifteen states and 98 PhD programs account for 72 percent of all history PhDs earned from 2004–13. These 15 states also employed 50 percent of those historians, a big number to be sure, but one that left room for them to “export” large numbers of PhDs to other states. California, for example, is home to over 600 historians, but awarded over 1,100 PhDs in the discipline. The states that “export” PhDs appear to send them to the Southeast and West, both regions that are home to more PhDs than were trained within their borders.
As you might expect, the careers historians build differ depending on where they live. Sometimes, it seems possible to speculate about why this might be. In California, for instance, only 38 percent of historians work in four-year tenure-track positions, while in South Dakota, over 80 percent do. South Dakota is one of the few states that does not host a PhD program, and it seems that few historians move there except for those who land tenure-track positions. In contrast, California’s high quality of life and diversified economy seem to attract them in large numbers. However, numbers at the state level vary significantly and often are complicated by small samples (as in the case of South Dakota, home to only 12 history PhDs in our cohort), making it difficult to draw firm conclusions.
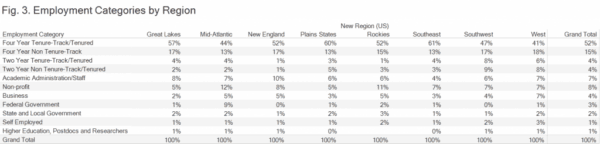
Seen regionally, PhD employment patterns begin to even out, though not without suggesting subtle variations in the regional economies. Tenure-track employment is most common in the Southeast, Great Plains, and Great Lakes, and least common in the far West. In contrast, non-tenure-track rates are relatively stable across regions, except in the West and Southwest, where over a quarter of history PhDs are employed in contingent positions. Outside the professoriate, historians disperse in slightly different directions as they take advantage of regional economic opportunities. In New England, PhDs find more opportunities in academic administration, while those out West are most likely to be employed in the private sector.
In general, PhDs working in large urban areas seem to be employed in more diverse jobs than those living in rural areas and college towns. Large cities tend to have lower rates of employment on the tenure track and are hubs for those working in the nonprofit and business sector. Cities also tend to have high rates of historians teaching off the tenure track.
No major city is more distinctive, though, than the District of Columbia. DC is home to only 700,000 residents and is a mere 68 square miles, but only five states employ more historians than the city. The 295 history PhDs we have located working here are remarkable not only for their density, but for their employment patterns, which look like nowhere else in the country. Over 75 percent of all historians employed by the federal government work in the District. Even so, fewer than half of DC’s history PhDs work for the federal government because the District is also a national hub for historians in the nonprofit and business sectors. Nine percent of all history PhDs employed by nonprofits work in in DC; only the State of New York employs more. Likewise, only California and New York employ more historians in the private sector than DC. In another dramatic departure from national averages, only 18 percent of DC historians work as postsecondary teachers compared to 75 percent who do so nationally.
Knowing where historians live raises important questions about the relationship between mobility and careers, a perennial, controversial, and poorly understood aspect of PhD culture. PhD candidates have long been told that their ability to find employment rests on their willingness to move anywhere in pursuit of a tenure-track job. Without question, many history PhDs appear to follow this path. However, department-level data (available in the forthcoming version of Where Historians Work) shows that in many departments, graduates cluster in the cities and regions where they receive their degrees. These geographies no doubt reflect hierarchies of prestige within the discipline: earlier studies of historical careers done by the AHA have found that graduates from high-prestige programs scatter more widely than those from ones with regional reputations, a pattern that seems to still hold true. The geographical data also highlights the existence of regional employment patterns that complicate our sense of a single national academic job market. More importantly, they suggest that many PhDs have ties of family, friendship, and circumstance in the regions where they earn their degrees, and build careers that reflect those roots. Our data speak to outcomes rather than motivations, but knowing more about where historians live is a crucial step towards untangling the question of why.
This post first appeared on AHA Today.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License. Attribution must provide author name, article title, Perspectives on History, date of publication, and a link to this page. This license applies only to the article, not to text or images used here by permission.